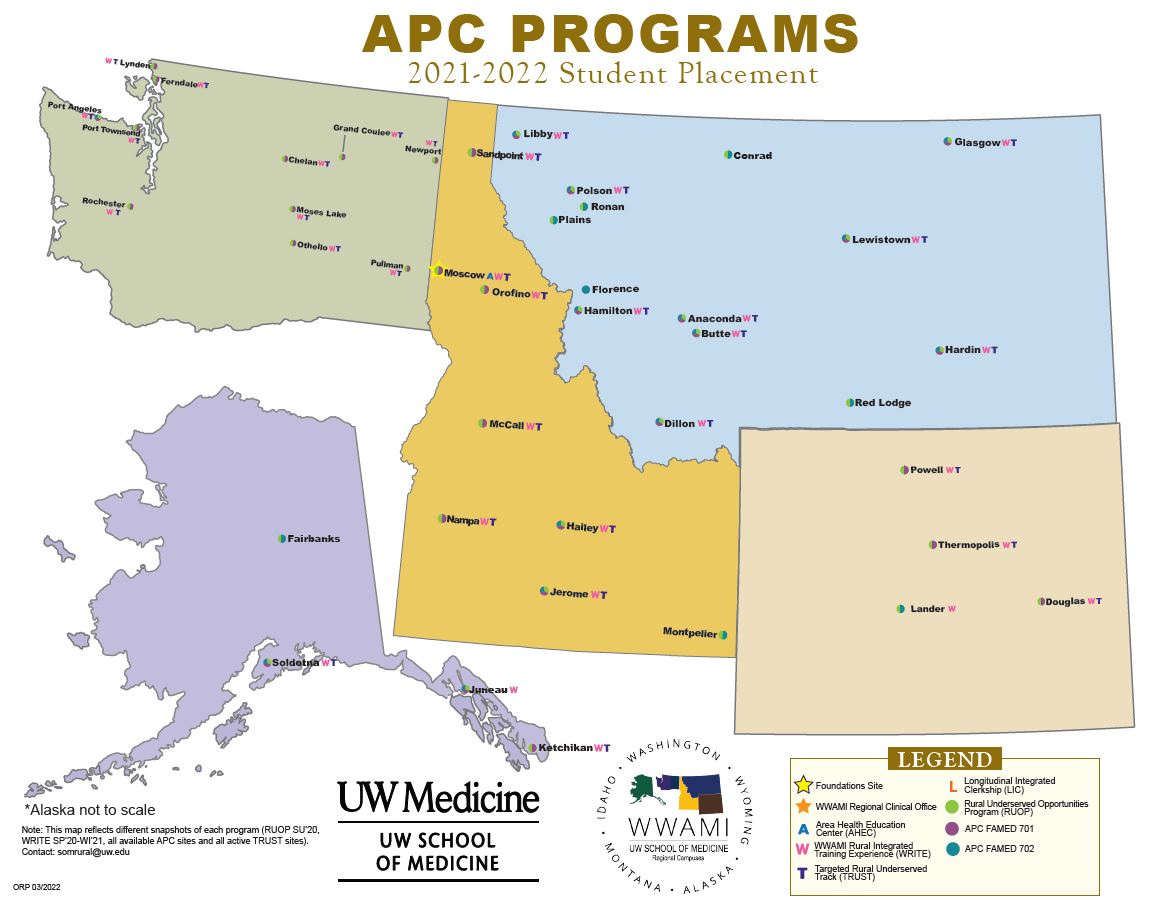
Rural FAMED APC
Rural Family Medicine Advanced Patient Care (FAMED APC)
Clerkship Overview
Rural Programs and the Department of Family Medicine Medical Student Education Section have developed an advanced patient care (APC) clerkship for medical students at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
These two clerkships, FAMED 701 and FAMED 702, are four-week rotations focusing on the care of rural communities, specifically in the outpatient setting, across WWAMI. Students are expected to function at the level of a beginning intern, taking primary responsibility for outpatient care, with appropriate supervision, to refine core clinical skills, expand medical knowledge, improve clinical reasoning, and work as an integral part of the clinical team. For more information contact us at somrural@uw.edu or see a list of contacts in our office.
Clerkship Goals
Clerkship Goals
- Take on primary responsibility for patient care with appropriate supervision
- Refine core clinical skills
- Improve clinical reasoning and expand medical knowledge
- Work as an integral part of the clinic team
- Apply concepts and skills from the longitudinal Ecology of Health & Medicine course in a relevant clinical setting
Clerkship Objectives
Students will achieve the following skills through patient care, simulation and/or other instructional methods:
- Gather a history and perform a physical examination
- History-taking skills
- Obtain both comprehensive and focused histories in an organized and timely fashion.
- Demonstrate patient-centered skills, cultural awareness, and humility.
- Demonstrate clinical reasoning in gathering focused information relevant to patient care.
- Physical examination techniques
- Perform both comprehensive and clinically relevant focused physical exams.
- Demonstrate patient-centered exam skills that respect privacy, comfort, and safety.
- Identify abnormal findings.
- History-taking skills
- Develop a prioritized differential diagnosis and select a working diagnosis following a patient encounter
- Collect and synthesize pertinent information based on prior records.
- Integrate new information as it emerges.
- Utilize evidence-based concepts for diagnosis and treatment.
- Discuss and document clinical reasoning contributing to the working diagnosis.
- Recommend and interpret common diagnostic and screening tests
- Incorporate high-value care principles as part of a care plan.
- Interpret basic test results.
- Elicit and incorporate patient preferences into recommendations.
- Enter and discuss patient orders/prescriptions
- Compose orders efficiently and effectively (eg. Selective use of order sets).
- Write prescriptions and attend to patient-specific factors (eg. age, weight, allergies).
- Discuss orders and prescriptions in a patient-centered manner.
- Provide documentation of a clinical encounter in written or electronic format
- Organize and prioritize information using a clear narrative.
- Update and organize problem list, working and differential diagnosis and plan.
- Document in a timely fashion.
- Document patient preferences into clinical decision-making.
- Provide an oral presentation/summary of a patient encounter
- Present accurate, concise, and well-organized information and acknowledge uncertainty.
- Adjust presentation to meet the needs of the listener.
- Assure closed-loop communication between presenter and receiver of information to confirm shared understanding.
Grade Anchors
Grade Anchors
Evaluation and the student’s final grade are based on the student’s performance of the clerkship. Review the anchors in each category and select the category that most closely mirrors the student’s performance in that area. Please refer to FM Grade Anchor and Evaluation Form for complete details.
- Clinical Knowledge and Skills
- Knowledge in Subject Area
- Data Gathering Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Patient Care Skills
- Integration Skills
- Management Skills
- Patient-Centered Care (PCC)
- Interpersonal Relationships
- Communication Skills
- Relationships with Patients and Families
- Professional Relationships
- Professional/Personal Characteristics
- Educational Attitudes
- Dependability and Responsibility